A statistically significant test result (P ≤ 005) means that the test hypothesis is false or should be rejected A P value greater than 005 means that no effect was observed How do you choose the null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis? 6 State whether the null hypothesis have been accepted or rejected Your report should be clearly structured and should include – Your matriculation number as a header – A title – An introduction (≤ 150 words) – A brief introduction to the report to describe what samples were analysed and what comparisons you look at in your reportTypically, if there was a 5% or less chance (5 times in 100 or less) that the difference in the mean exam performance between the two teaching methods (or whatever statistic you are using) is as different as observed given the null hypothesis is true, you would reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis Alternately, if the chance was greater than 5% (5 times in 100

What Are Type I And Type Ii Errors Simply Psychology
It tells whether the hypothesis be accepted or rejected
It tells whether the hypothesis be accepted or rejected- The significance test is the process used, by researchers, to determine whether the null hypothesis is rejected, in favor of the alternative research hypothesis, or notA after testing a hypothesis, a conclusion can be drawn on whether it will be accepted or rejected B after testing an observation, a conclusion can be drawn on whether it will be accepted or rejected C after testing a conclusion, it can be predicted whether a hypothesis will be



Hypothesis Testing Statistically Significant P Value
The answer to the question why is this It can be rejected at a later date because it is This result tells us that it is unlikely that the differences in the population are zero The Note that the confidence intervals also transmit information regarding whether the null hypothesis should be rejected or retained If the hypothesized difference between the means (0) falls outside of the confidence limits, we can reject the null hypothesis 6 Here, I useConclusion Determination of whether the hypothesis should be
I actually realised i made a mistake in my experiment yesterday, so Why can an accepted hypothesis be rejected at a later date? Thus, the null with c1 and c2 cannot be rejected (ie we do not know whether it has or not) Whereas the null with c3 can be rejected Ie at c3 there is a significant effect on z As already mentioned, a null is never accepted, we either reject, or fail to reject Thank you!
State whether the null hypothesis is accepted or rejected based on the ANOVA results Oneway ANOVA of 'Education' variable with the 'Salary' variable 퐻 0 The means of 'Education' variable with respect to each Salary is equal 퐻 1 At least one of the means of 'Education' variable with respect to each Salary is unequal The significance test is the process used, by researchers, to determine whether the null hypothesis is rejected, in favor of the alternative research hypothesis, or notTranscribed image text 14 Which statement is correct about the scientific method process?



Data Analysis In The Geosciences



Hypothesis Testing Statistically Significant P Value
It is said that hypothesis is either rejected or accepted as true Is this true?Personally, I would avoid saying "the alternative hypothesis was accepted" because this implies that you have proven the alternative hypothesis to be true Generally, one study cannot "prove" anything, but it can provide evidence for (or against) a hypothesis Additionally, the concept of challenging or "falsifying" a hypothesis is stronger than "proving" a hypothesis (for more – State whether the null hypothesis has been accepted or rejected and explain what this means in the context of the samples that you analysed – Conclusion (≤ 150 words) – Brief conclusion to summarise the findings of your experiment and analysis




A Null Hypothesis Can Only A Be Accepted B Chegg Com
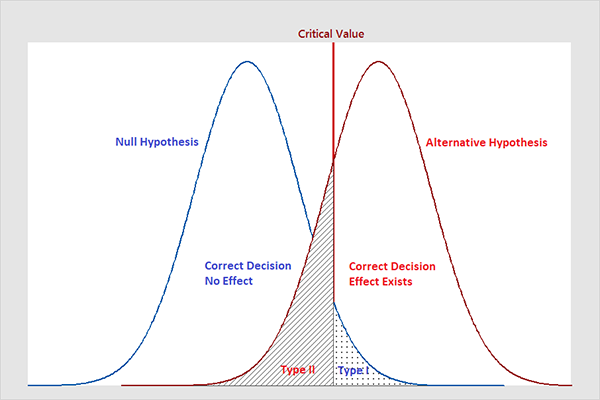



Types Of Errors In Hypothesis Testing Statistics By Jim
Hypothesis testing shows whether the hypothesis should be accepted or rejected It has been rightly said that "You torture the data until they confess" This paper include the introduction, steps of hypothesis testing, function of hypothesis and testing of hypothesis KEYWORDS Research, Hypothesis, null hypothesis, alternate hypothesis, population, significance INTRODUCTION 6 State whether the null hypothesis have been accepted or rejected Your report should be clearly structured and should include – Your matriculation number as a header – A title – An introduction (≤ 150 words) – A brief introduction to the report to describe what samples were analysed and what comparisons you look at in your reportHypothesis Essential #2 Testability (Provability) A hypothesis must be testable to qualify as a scientific hypothesis If it's not testable, it's not a hypothesis Testability means that you must be able to collect observable data in a scientifically rigorous fashion to assess whether it supports the hypothesis or not



2




123 Hypothesis Testing An Example Hypothesis Testing Situation
The purpose of the one sample ttest is to determine if the null hypothesis should be rejected, given the sample data Here we will perform two tailed (or two sided) one sample t test Hypothesis Testing Definition The Hypothesis Testing is a statistical test used to determine whether the hypothesis assumed for the sample of data stands true for the entire population or not Simply, the hypothesis is an assumption which is tested to determine the relationship between two data sets In hypothesis testing, two opposingTranscribed Image Textfrom this Question A after testing a hypothesis, a conclusion can be drawn on whether it will be accepted or rejected B after testing an observation, a conciusion can be drawn on whether it wil be accepted or rejected C, after testing a conclusion, it can be predicted whether a hypothesis will be accepted or rejected 44
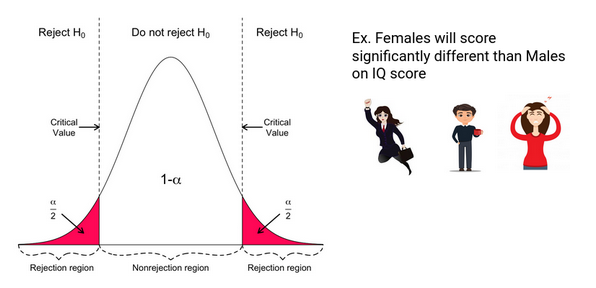



Hypothesis Testing Difference Between Z Test And T Test




Review Estimating A Mean Suppose We Want To
By definition, an accepted hypothesis is what you are left with once H0 has been disproven, This is also called H1 Importantly, H1 has not not been but emerges from the ruins of the disproven H0 A rejected hypothesis should always be the state of not having been able to disprove H0 Any other use of the term will easily get you into trouble Why can an accepted hypothesis be rejected at a later date?In hypothesis testing if the null hypothesis is rejected, a no conclusions can be drawn from the test b will always be accepted at the 1% level c may be rejected or not rejected at the 1% level d None of the above c may be rejected or not rejected at the 1% level If a hypothesis is not rejected at a 5% level of significance, it will a also not be rejected at the 1% level b always




P Value And Statistical Significance Simply Psychology



1
Statistical significance uses a scientific method to help determine whether a hypothesis can be accepted or rejected As such, it gives readers confidence that the reported difference is actually true as it is based on a scientific concept, rather than human judgement However, despite its ability to interpret differences in statistical data, it fails to tell us the magnitude of thisAnswer to If the hypothesis test for correlation is found to be significant (ie, we rejected the null hypothesis/accepted the alternate My concern here is similar to my issues with null hypothesis statistics testing 1 Hypotheses in social science are vague enough that it's just about never clear what it would mean for a hypothesis to be "confirmed" or "rejected" There are no true zeroes, and even when it comes to estimation, the size and direction of comparisons can vary across people and



2
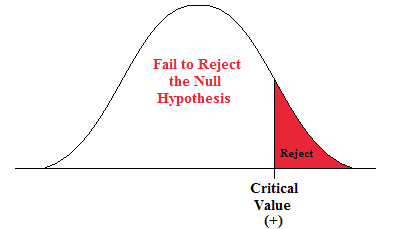



Chapter 3 Hypothesis Testing Natural Resources Biometrics
the summarized results from the experiment will determine whether the hypothesis is accepted or rejected and that is where you blankThe rule for the proper formulation of a hypothesis test is that the alternative or research hypothesis is the statement that, if true, isInterpret the statistical results against the null hypothesis and state whether it is accepted or rejected Step 4 Write Section 4 of the DAA Statistical Conclusions Provide a brief summary of your analysis and the conclusions drawn about this ttest Analyze the limitations of the statistical test and/or possible alternative explanations for your results Step 5 Write Section 5 of the
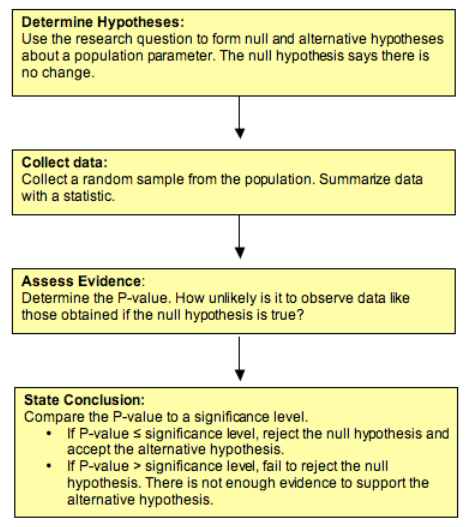



Hypothesis Testing 3 Of 5 Concepts In Statistics



Importance Of Hypothesis Testing In Data Science
A decision about whether the null hypothesis should be rejected Test Value (test statistic) – the numerical value obtained from a statistical test **Each statistical test that we will look at will have a different formula for calculating the test value In reality, the null hypothesis may or may not be true, and a decision is made to reject or not reject it on the basis of the data Central Limit Theorem States that with a large enough sample, the sample mean will be normally distributed A normally distributed sample mean is necessary to apply the ttest, so if you are planning to perform a statistical analysis of experimental data, it's important to have a sufficiently large sample;Depending on the situation the null hypothesis is either accepted or its is rejected If the null hypothesis is not accepted than alternate hypothesis is accepted The null hypothesis is used to test the significance of differences Basically it tells that the result would have been the same based on play of chanceTo understand what a null hypothesis is, consider the following




Hypothesis Testing Maths Libguides At La Trobe University




Hypothesis Testing For Means Proportions
Why is a hypothesis supported or rejected, rather than being proven true or false?The pvalue is a descriptor of the test itself The pvalue tells us "how good" the test is (in a certain sense of "how good"), even before the we perform the test;Yes, it can It can also be neither accepted nor false If no errors are made, it will not be rejected if true However, a hypothesis is not usually accepted Statistical analysis of experimental results yield a confidence score that If the null hypothesis is not rejected, then we must be careful to say what this means The thinking on this is similar to a legal verdict Just because a person has been declared "not guilty", it does not mean that he is innocent In the same way, just because we failed to reject a null hypothesis it does not mean that the statement is true For example, we may want to investigate




Hypothesis Testing Difference Between Z Test And T Test
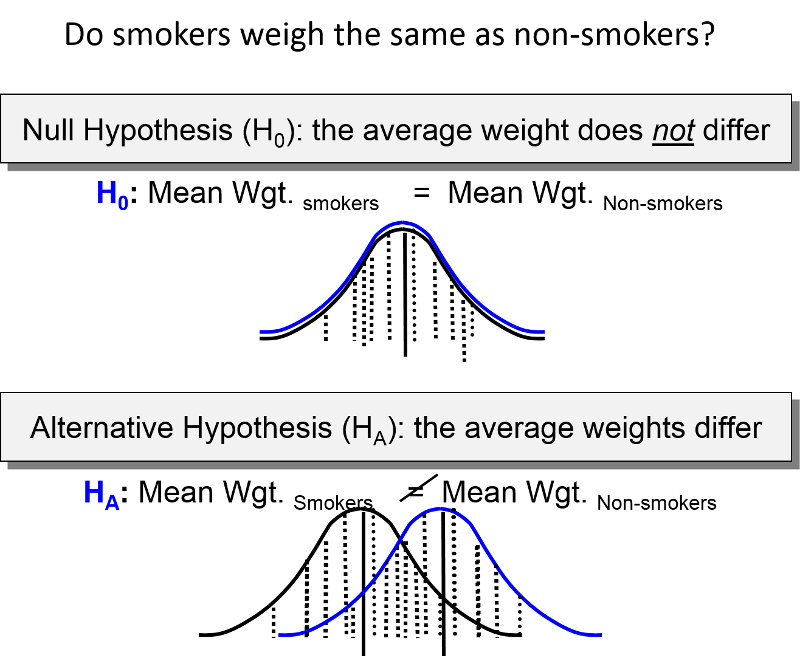



Hypothesis Testing
A comparison of the two P values determines whether the null hypothesis is rejected or accepted If the P value The null hypothesis is either accepted or rejected in terms of the given data If Pvalue is less than α, then the null hypothesis is rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis, and if the Pvalue is greater than α, then the null hypothesis isThe answer to the question why is this It can be rejected at a later date because it is falsifiable in nature if it is a good hypothesis If you meant to ask HOW it can be rejected, the answer is by way of further experimentation that rules out some or all of the hypothesis as stated



Chapter 10 Introduction To Hypothesis Testing Fundamental Statistics
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/HypothesisTestinginFinance4-deefaac530e74d2880cf92a461b4c1fb.png)



Hypothesis Testing In Finance Concept And Examples
The null hypothesis is rejected if the value of F falls outside the range defined by the critical value of the Fdistribution An Ftest is used to test if the variances of two populations are equal Thus, the null hypothesis is that the two variances are equal H_o sigma_1^2 = sigma_2^2 The statistic we define to test this is the ratio of the two variances F = s_1^2/s_2^2 Where s_1Rejection rule It is a criterion under which a hypothesis tester decides whether a given hypothesis must be accepted or rejected The general rule of thumb is that if the value of test statics is greater than the critical value then the null hypothesis is rejected in the favor of the alternate hypothesisTells wether the hypothesis be accepted or rejected 1 See answer gpalisoc6 gpalisoc6 Answer acceptedpa brainliest Explanation
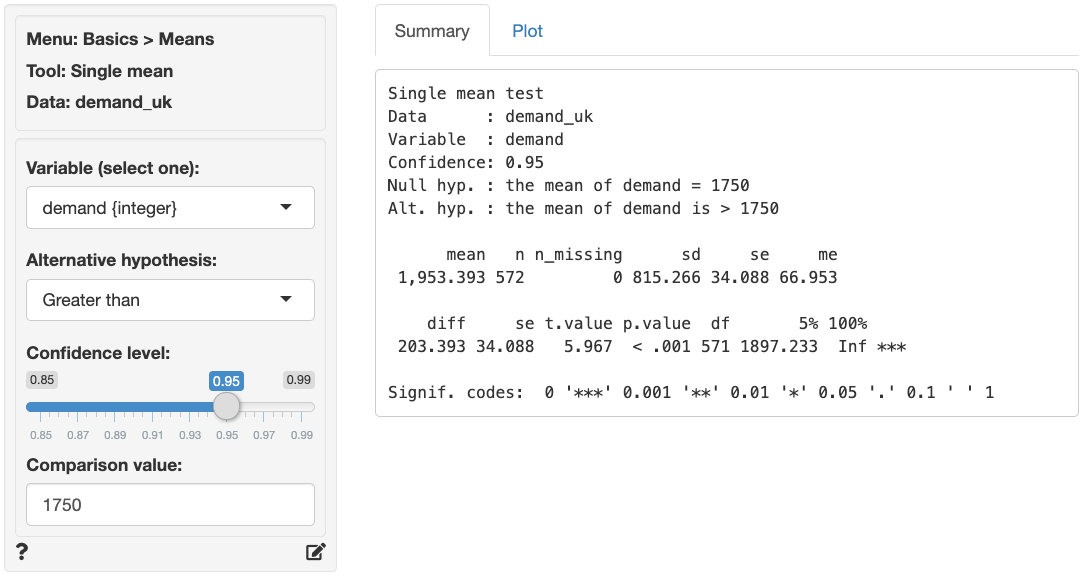



Basics Means Single Mean



2
No Whoever said it is mistaken Can't a hypothesis be neither rejected nor true?Correct answers 1, question It tells wether the hypothesis be accepted or rejectedOf the test, that is whether it is two, right, or lefttail If the test statistic is in the unlikely region identified by the critical value then the null hypothesis is rejected at the associated significance level Reject the null hypothesis, Ho, if P



Frontiers When Null Hypothesis Significance Testing Is Unsuitable For Research A Reassessment Human Neuroscience




Inferential Statistics Ppt Download
Start studying Chem Chapter 1 Self Assessment Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools Given α=005 and the test statistics, decide whether the null hypothesis is to be rejected or accepted 0131 Answers 1 See answers Iba pang mga katanungan Math Math, 19, hajuyanadoy What is the xintercept of the line with this equation −2x1/2y=18 Kabuuang mga Sagot 3 magpatuloy Math, 1928, abyzwlye What is the answer of




Examples Identifying Type I And Type Ii Errors Video Khan Academy
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/HypothesisTestinginFinance1_2-1030333b070c450c964e82c33c937878.png)



Hypothesis Testing In Finance Concept And Examples




One Tailed And Two Tailed Hypothesis Tests Explained Statistics By Jim



Some Basic Null Hypothesis Tests Research Methods In Psychology 2nd Canadian Edition
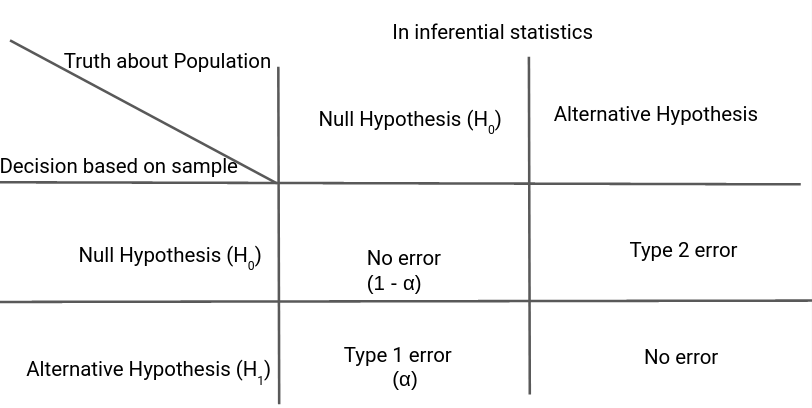



Hypothesis Testing Difference Between Z Test And T Test
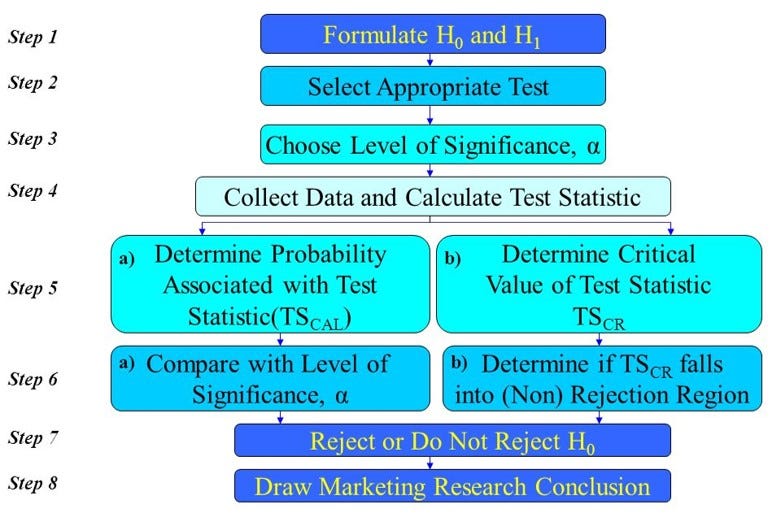



Everything You Need To Know About Hypothesis Testing Part I By Mahesh Towards Data Science
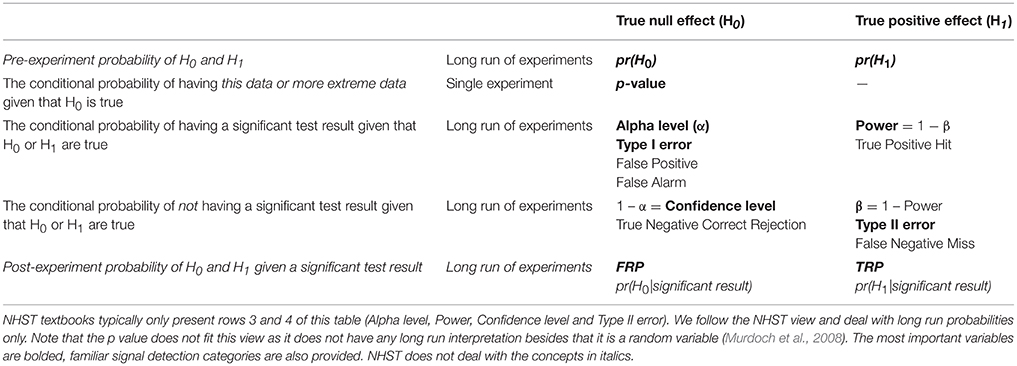



Frontiers When Null Hypothesis Significance Testing Is Unsuitable For Research A Reassessment Human Neuroscience
/null-hypothesis-vs-alternative-hypothesis-3126413-v31-5b69a6a246e0fb0025549966.png)



Null Hypothesis And Alternative Hypothesis




Statistics Rd Wi Fo R E T A
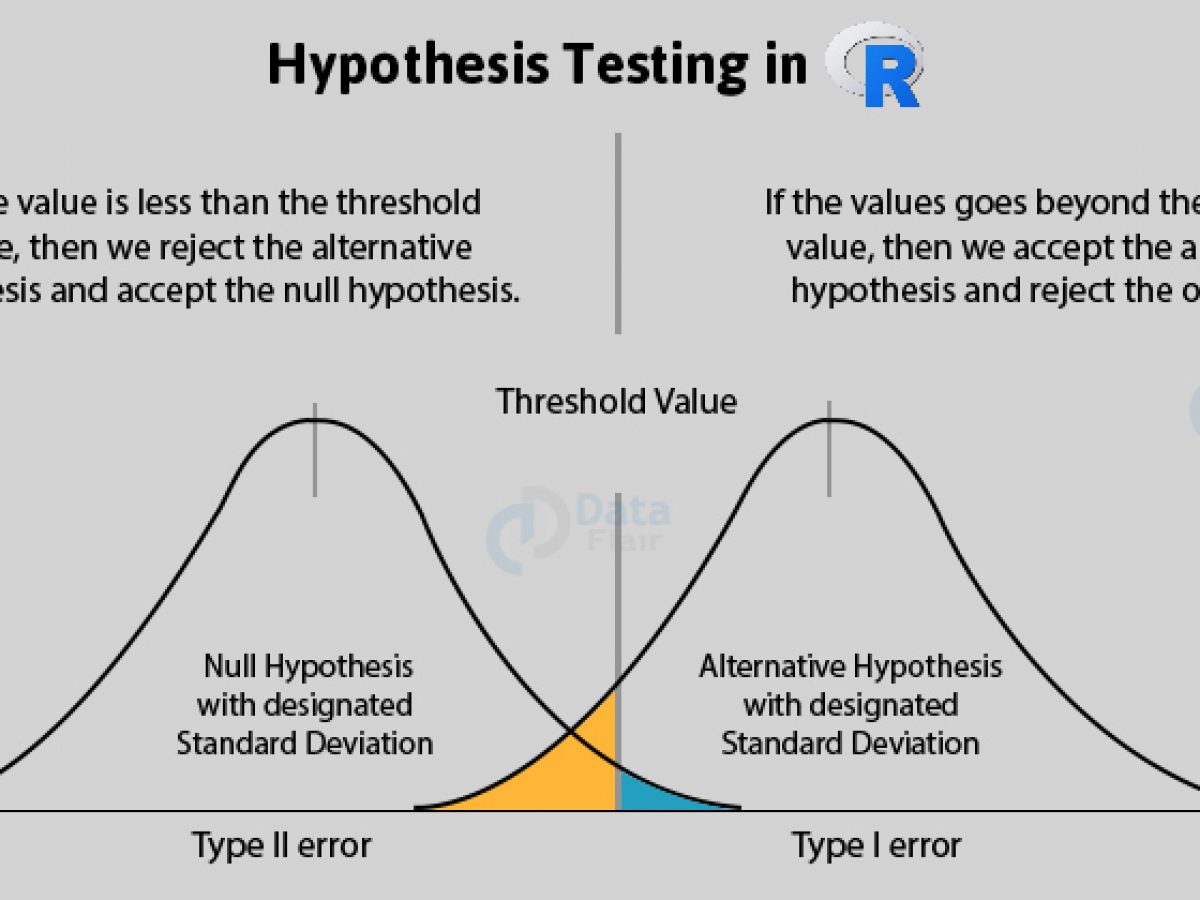



Introduction To Hypothesis Testing In R Learn Every Concept From Scratch Dataflair
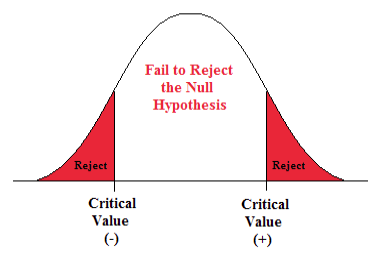



Chapter 3 Hypothesis Testing Natural Resources Biometrics




6 Hypothesis Testing Marketing Research Design Analysis 21




Failing To Reject The Null Hypothesis Statistics By Jim
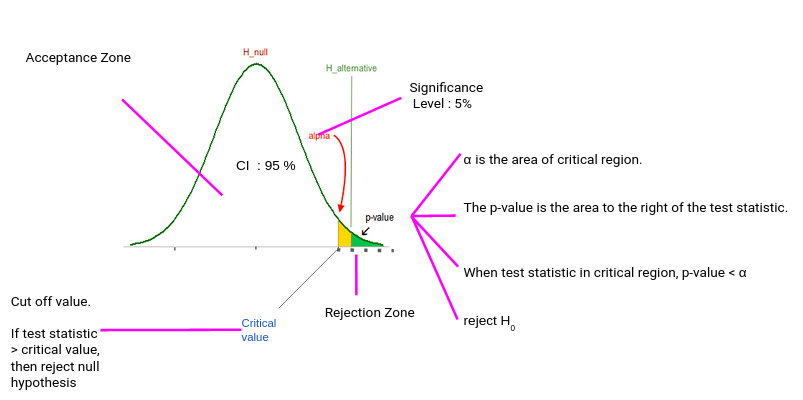



Hypothesis Testing Difference Between Z Test And T Test
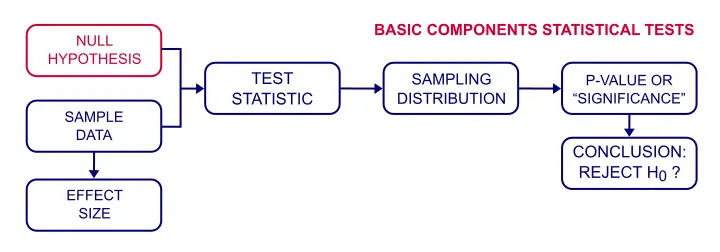



Null Hypothesis Quick Introduction
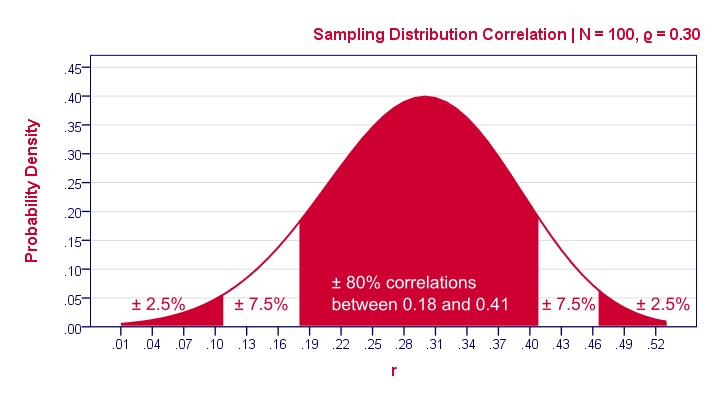



Null Hypothesis Quick Introduction




In Hypothesis Testing A Test Statistic Is O The Chegg Com
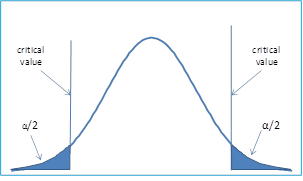



Null And Alternative Hypothesis Real Statistics Using Excel
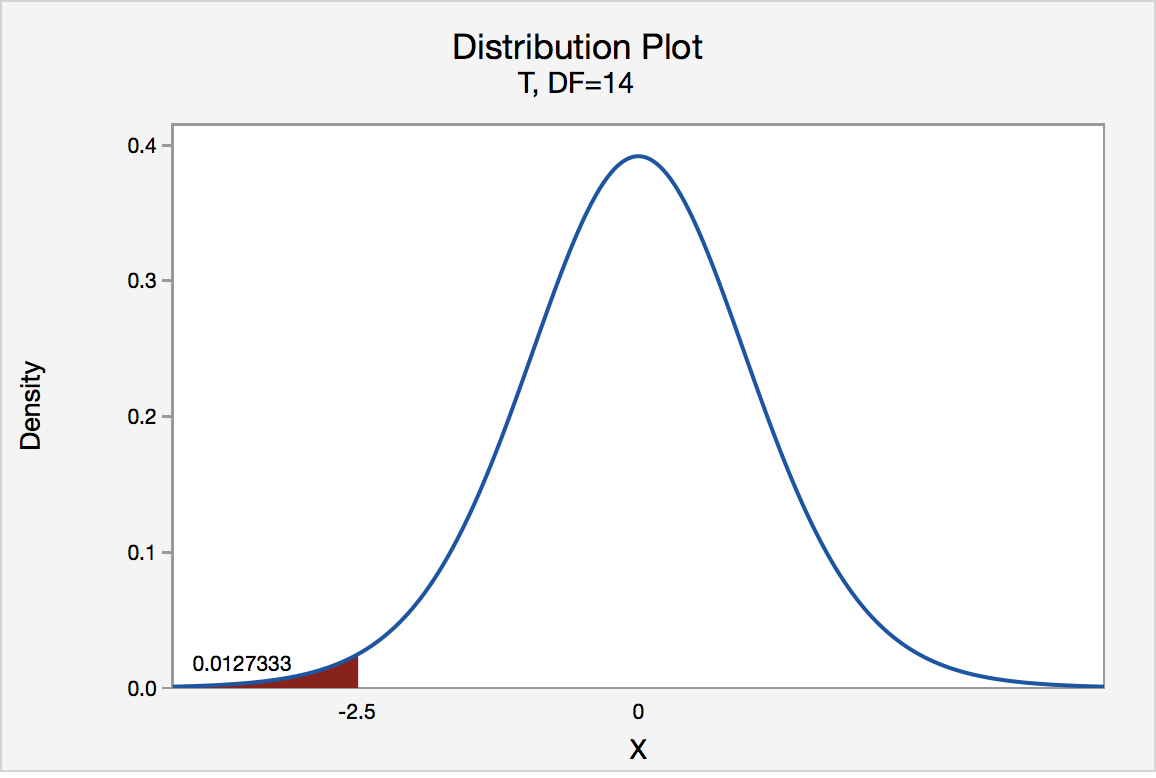



S 3 2 Hypothesis Testing P Value Approach Stat Online
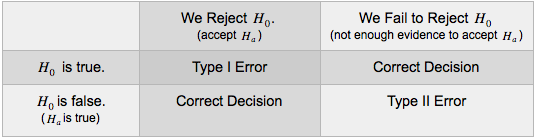



Hypothesis Testing 5 Of 5 Concepts In Statistics



Hypothesis Testing Handbook Of Biological Statistics




Hypothesis Testing Significance Level And Rejection Region 365 Data Science




Everything You Need To Know About Hypothesis Testing Part I By Mahesh Towards Data Science
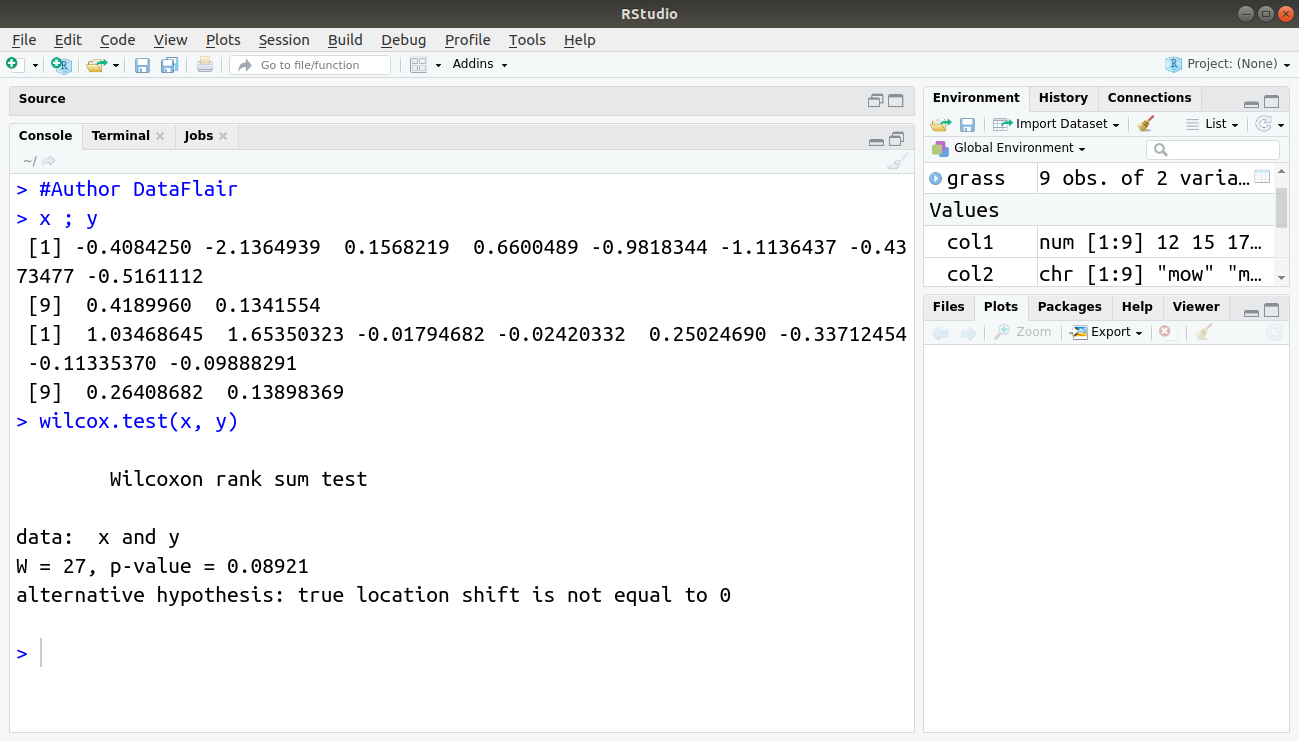



Introduction To Hypothesis Testing In R Learn Every Concept From Scratch Dataflair




How To State The Conclusion About A Hypothesis Test Dawn Wright Ph D




Hypothesis Testing All A Beginner Needs To Know By Abhishek Barai Analytics Vidhya Medium




Hypothesis Testing P Value A Simplified Approach By Suraj Gurav Towards Data Science
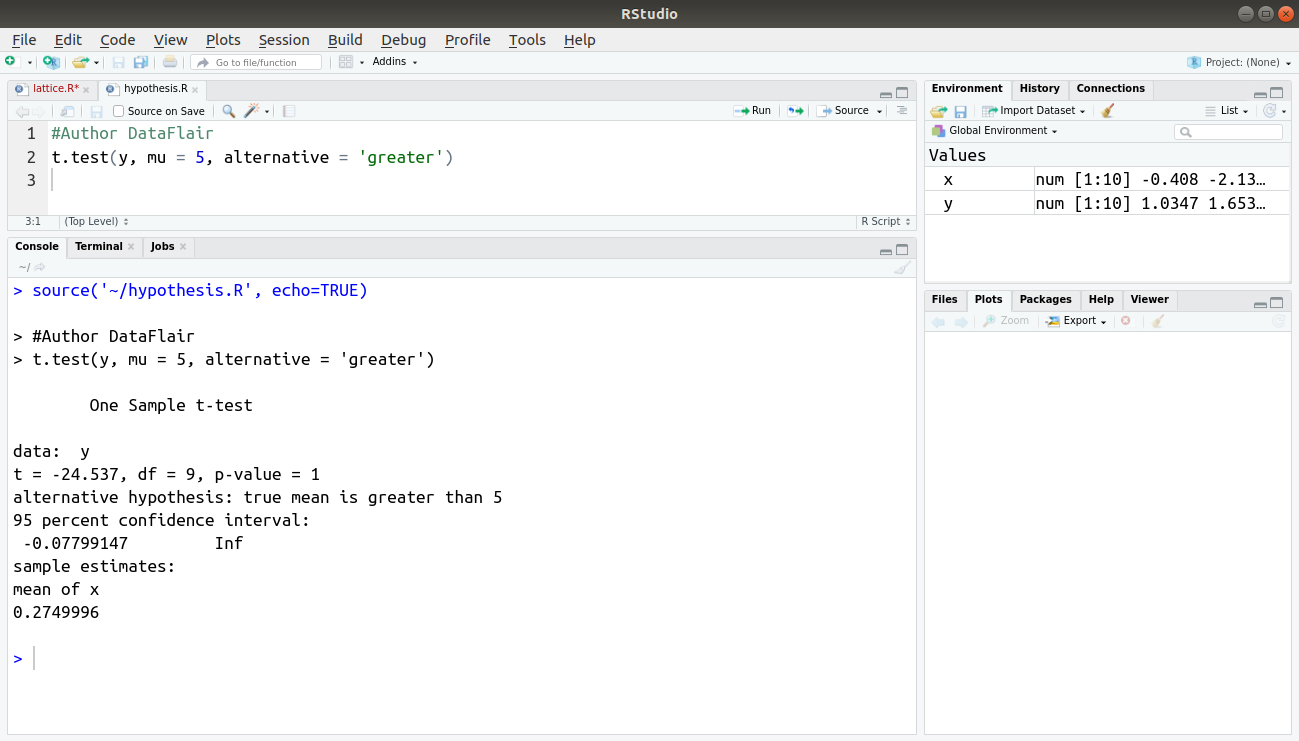



Introduction To Hypothesis Testing In R Learn Every Concept From Scratch Dataflair




Hypothesis Testing Tool



Data Analysis In The Geosciences
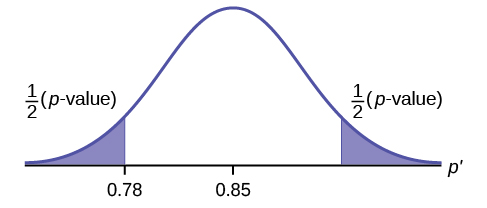



Full Hypothesis Test Examples Introductory Business Statistics
/HypothesisTestinginFinance1_2-1030333b070c450c964e82c33c937878.png)



Hypothesis Testing In Finance Concept And Examples




Hypothesis Wikipedia




Hypothesis Testing And P Values Video Khan Academy
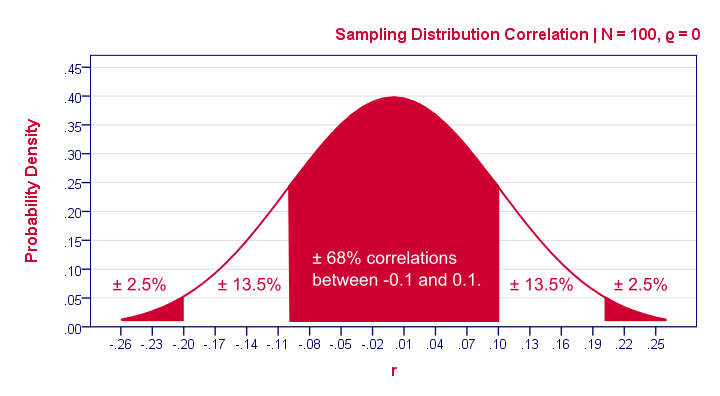



Null Hypothesis Quick Introduction




Solved A After Testing A Hypothesis A Conclusion Can Be Chegg Com
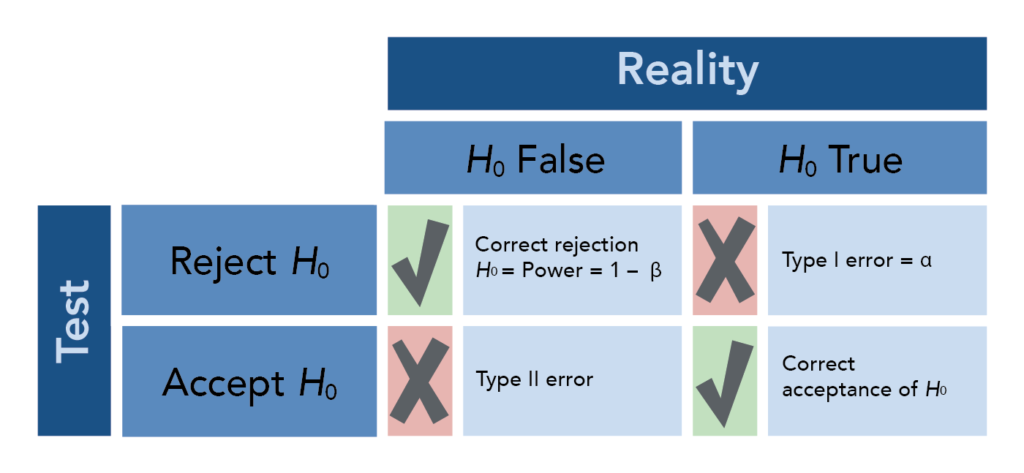



Hypothesis Testing 5 Of 5 Concepts In Statistics




Master Hypothesis Testing In Statistics Guide




Hypothesis Testing Significance Level And Rejection Region 365 Data Science
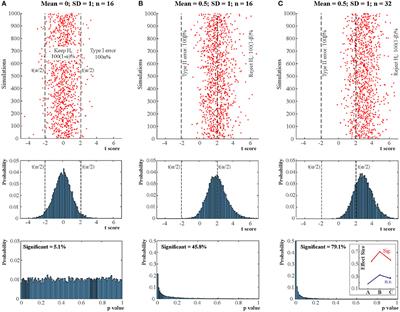



Frontiers When Null Hypothesis Significance Testing Is Unsuitable For Research A Reassessment Human Neuroscience
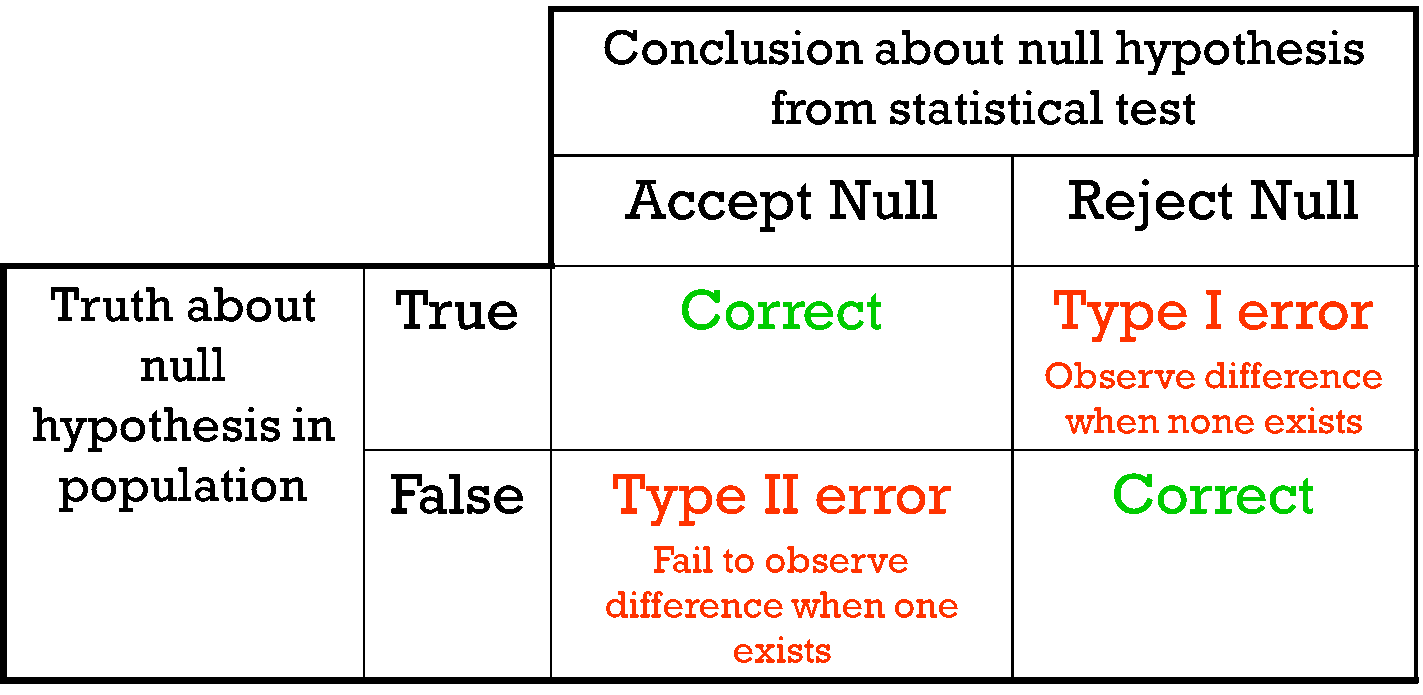



Hypothesis Testing Maths Libguides At La Trobe University



1



Hypothesis Testing Problems Z Test T Statistics One Two Tailed Tests 2 Youtube



2




A8yqq Fj1d8bwm




Understanding Type I And Type Ii Errors



2



1




P Value And Statistical Significance Simply Psychology
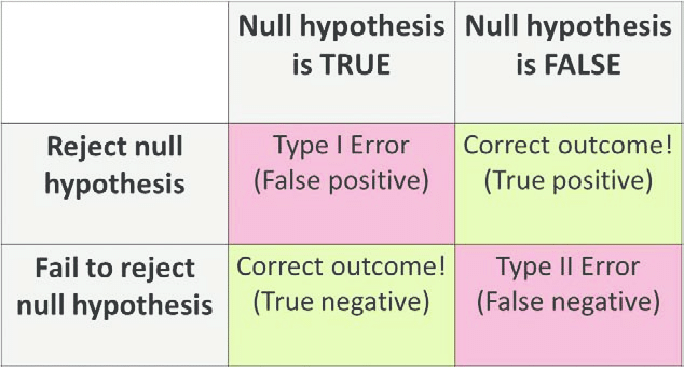



Hypothesis Testing Statistically Significant P Value
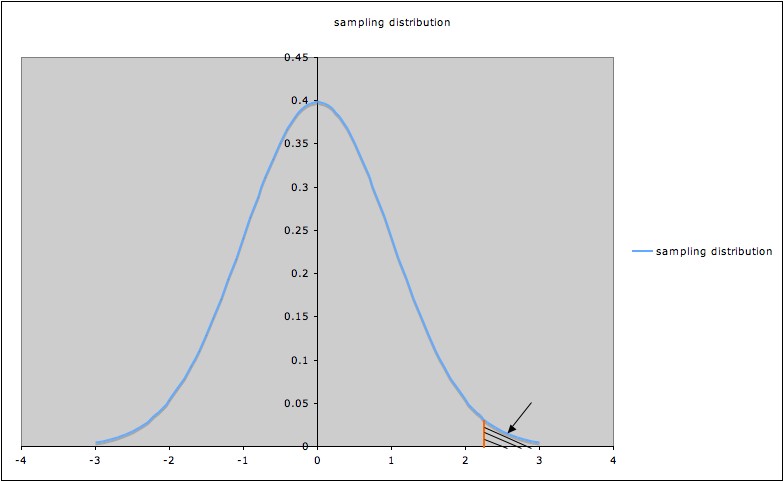



Rejection Region Critical Region For Statistical Tests Statistics How To
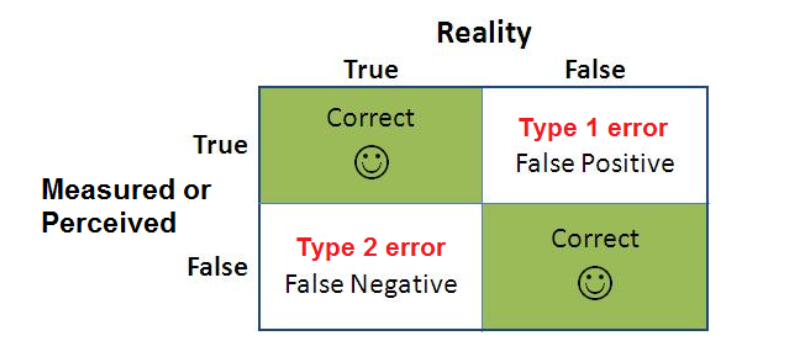



Everything You Need To Know About Hypothesis Testing Part I By Mahesh Towards Data Science




Hypothesis Testing Significance Level And Rejection Region 365 Data Science



Hypothesis Testing Calculator



2
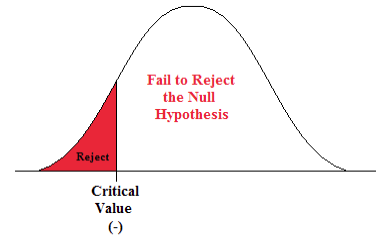



Chapter 3 Hypothesis Testing Natural Resources Biometrics




Solved 1 A Statistical Hypothesis Is A Conjecture About A Chegg Com




Frontiers When Null Hypothesis Significance Testing Is Unsuitable For Research A Reassessment Human Neuroscience




Chapter 10 Summary Stat213 Chapter 10 Hypothesis Testing Using A Single Sample 10 1 Hypotheses Studocu



1




Hypothesis Testing Critical Values Rejection Regions I Statistics 101 4 Marinstatslectures Youtube




Null Hypothesis Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary




Ap Statistics More About Tests And Intervals Ppt Download




Comparing P Values To Different Significance Levels Video Khan Academy




Null Hypothesis And Alternative Hypothesis With 9 Differences




Hypothesis Testing Maths Libguides At La Trobe University
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/HypothesisTestinginFinance2_2-8b3d4def38c945e8940385f1382b7ec4.png)



Hypothesis Testing In Finance Concept And Examples



Data Analysis In The Geosciences




Accept Or Reject Null Hypothesis Youtube
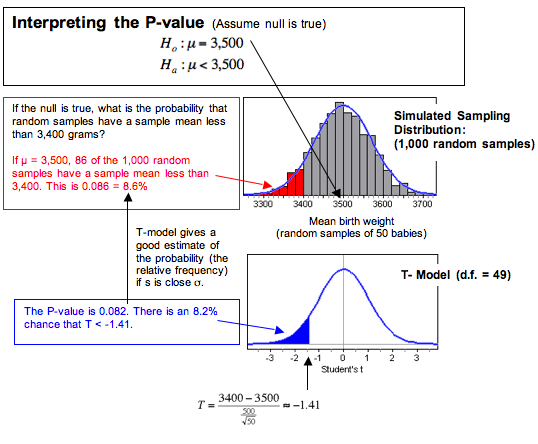



Hypothesis Test For A Population Mean 5 Of 5 Concepts In Statistics




What Are Type I And Type Ii Errors Simply Psychology




Jpma Journal Of Pakistan Medical Association



Ocf Berkeley Edu
/hypothesis-classroom-board-479946192-831928db59dd47f2a8eec7e005dc8781.jpg)



Hypothesis Testing Definition




Hypothesis Testing Significance Level And Rejection Region 365 Data Science




Null Hypothesis Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
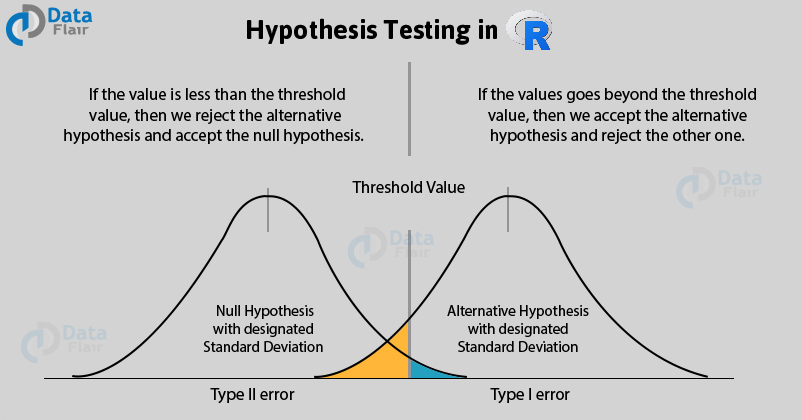



Introduction To Hypothesis Testing In R Learn Every Concept From Scratch Dataflair




Failing To Reject The Null Hypothesis Statistics By Jim




Type I And Ii Errors And Significance Level Krista King Math Online Math Tutor
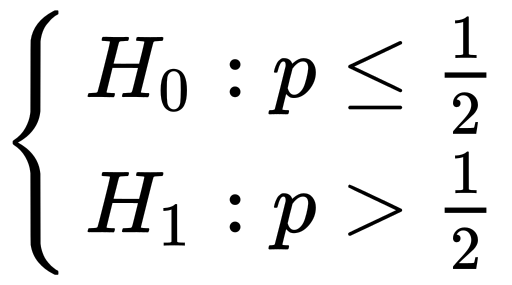



Hypothesis Testing Demystified How To Translate Math Into Plain By Dorian Lazar Towards Data Science



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿