Explanation Use the power rule and implicit differentiation to find the derivative d dx (x2 3 y2 3) = d dx (1) d dx (x2 3) d dx (y2 3) = d dx (1) Since we're differentiating with respect to x, we must put dy dx at every y term that we differentiate (after differentiating, of course) 2 3 x− 1 3 2 3y−1 3( dy dx) = 0 The differential equations y dx (x – y^2) dy = 0 find the general solution asked in Differential Equations by Beepin ( 587k points) differential equationsFind dy/dx y=3^x y = 3x y = 3 x Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y) = d dx (3x) d d x ( y) = d d x ( 3 x) The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′ y' y ′ Differentiate using the Exponential Rule which states that d dx ax d d x a x is axln(a) a x ln ( a) where a a = 3 3 3xln(3) 3 x ln ( 3)

Math 432 Hw 2 5 Solutions Pdf Free Download
Dy/dx=(y-1)(x-2)(y 3)/(x-1)(y-2)(x 3)
Dy/dx=(y-1)(x-2)(y 3)/(x-1)(y-2)(x 3)-Calculus Find dy/dx y^2= (x1)/ (x1) y2 = x − 1 x 1 y 2 = x 1 x 1 Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y2) = d dx ( x−1 x1) d d x ( y 2) = d d x ( x 1 x 1) Differentiate the left side of the equation Tap for more stepsCalculus Find dy/dx y=x^25x y = x2 − 5x y = x 2 5 x Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y) = d dx (x2 −5x) d d x ( y) = d d x ( x 2 5 x) The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′ y' y ′ Differentiate the right side of the equation Tap for more steps



Using Euler Rsquo S Method Find An Approximate Value Of Corresponding To 1 Given That Dy Dx X 2 Y And Y 1 When X 0 Use The Step Size H 0 25
Steps for Solving Linear Equation ( x ^ { 3 } y ^ { 2 } ) d x 3 x y ^ { 2 } d y = 0 ( x 3 y 2) d x − 3 x y 2 d y = 0 To multiply powers of the same base, add their exponents Add 2 and 1 to get 3 To multiply powers of the same base, add their exponents Add 2 and 1 to get 3Solved 3 (1x^2)dy/dx=2xy (y^31) Cheggcom math other math other math questions and answers Ex 94, 3 For each of the differential equations in Exercises 1 to 10, find the general solution 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥𝑦=1(𝑦≠1) 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥𝑦=1 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=1−𝑦 𝑑𝑦 = (1 − y) dx 𝑑𝑦/(1 − 𝑦) = dx 𝑑𝑦/(𝑦 − 1) = −dx Integrating both sides ∫1 〖𝑑𝑦/(𝑦 − 1)=〗 ∫1 〖−𝑑𝑥〗 log (y − 1) = −x C y − 1 = e(−
1 1 y dy dx = x2 ∫ 1 1 y dy dx dx = ∫ x2 dx ∫ 1 1 y dy = ∫ x2 dx ln(1 y) = x3 3 C 1 y = ex3 3 C = ex3 3 eC = Cex3 3 y = Cex3 3 −1 Applying the IV 3 = Ce0 −1 = C −1 ⇒ C = 4 y = 4ex3 3 −1 However we can perform a transformation to remove the constants from the linear numerator and denominator Consider the simultaneous equations {x 2y −3 = 0 2x y −3 = 0 ⇒ {x = 1 y = 1 As a result we perform two linear transformations Let {u = x −1 v = y −1 ⇔ {x = u 1 y = v 1 ⇒ ⎧⎨⎩ dx du = 1 dy dv = 1 And if we So, for the given example, we see that we will use the power rule on the lefthand side On the right, don't be misled by the twothirds power a2 3 is still a constant d dx (x2 3 y2 3) = d dx a2 3 Power rule 2 3 x− 1 3 2 3y−1 3 dy dx = 0 Multiply both sides by 3 2 x− 1 3 y− 1 3 dy dx = 0 1 x1 3 1 y1 3 dy dx = 0
For any differential equation, first figure out dy/dx and then try to identify which category this particular DE falls into We can see that the degree of both x and y is 1 So, you can either apply homogeneous or variable separable But you can2x1 2ydydx 0 may be written as 2x 2yy 0 and y xy2 y 2x 2y a 3 dydx y 2dx 2ydx x from ABOUT 063 at St John's UniversityThe general solution of the differential equation √(1 x^2 y^2 x^2y^2) xy(dy/dx) = 0 is (where C is a constant of integration) asked in Mathematics by Anjali01 ( 476k points)




Chapter Differentiation Questions 1 Find The Value Of Answers 1 2 If F X 2 2x 5 Find F 2 Answers 2 3 If Y 2s And X 2s 1 Ppt Download



Using Euler Rsquo S Method Find An Approximate Value Of Corresponding To 1 Given That Dy Dx X 2 Y And Y 1 When X 0 Use The Step Size H 0 25
Simple and best practice solution for (xy1)dx(2x2y3)dy=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homeworkInt (x^3)/y dy dx y=x^2 to y=x^(1/2) x=0 to 1 Extended Keyboard;Solve the differential equation dy/dx= ( (y1) (x2)* (y3))/ ( (x1) (y2)* (x3)) Group the terms of the differential equation Move the terms of the y variable to the left side, and the terms of the x variable to the right side Simplify the expression \frac {y2} {y1}\frac {1} {y3}dy Simplify the expression \frac {x2} {x1}\frac {1




Differential Equations Class 12 Ncert Solutions



Solve The Linear Differential Equation Dy Dx 3y X 1 X 2 Given That Y 2 When X 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Question Dy/dx = Y^2 Sin X^2, Y (2) = 1/3 This problem has been solved!Free separable differential equations calculator solve separable differential equations stepbystepSolve the Bernoulli equation {eq}\displaystyle \frac{dy}{dx} = y (xy^3 1) {/eq} Solution of Differential equation The given differential equation is a first order linear differential equation
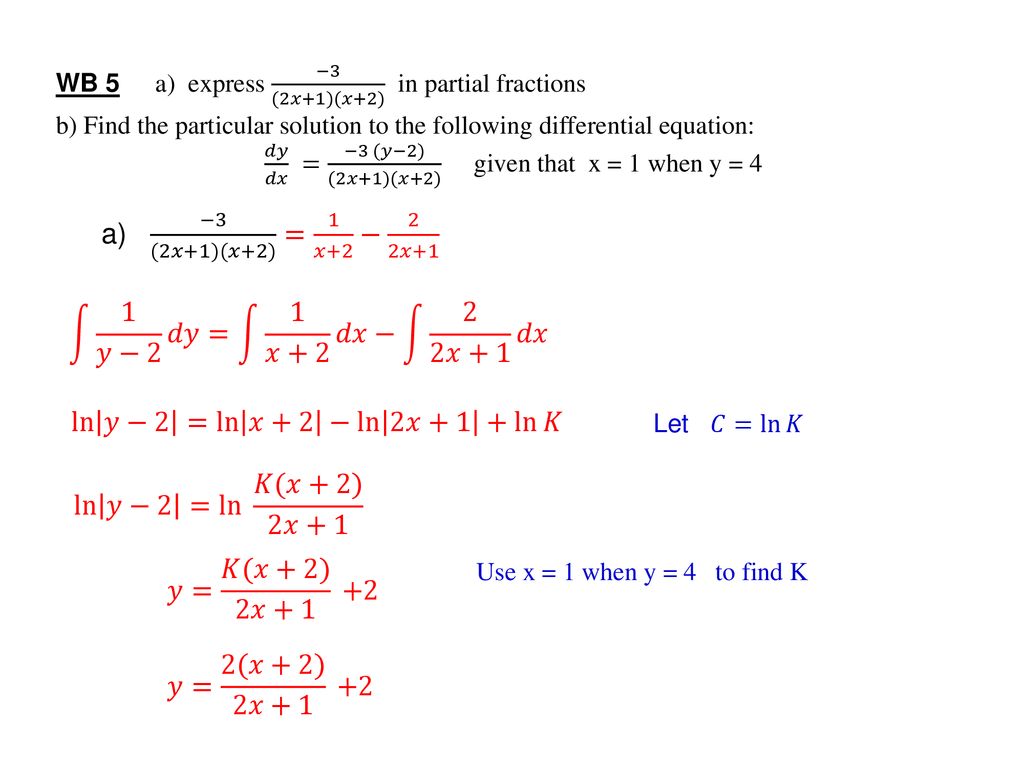



Differential Equations Ppt Download
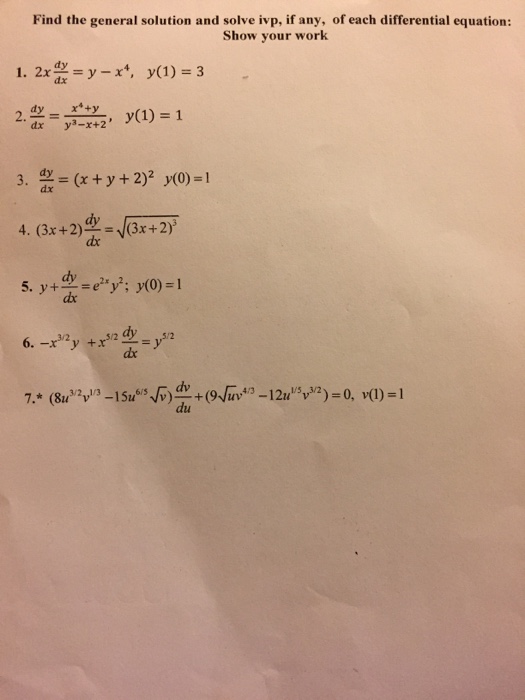



Find The General Solution And Solve Ivp If Any Of Chegg Com
Solve x (x – 1) dy/dx – (x – 2) y = x3 (2x – 1) Welcome to Sarthaks eConnect A unique platform where students can interact with teachers/experts/students to getGiven x 2/3 y 2/3 = a 2/3 y 2/3 = a 2/3 – x 2/3 Differentiate wrtx (2/3)y 1/3 dy/dx = 0 – (2/3)x 1/3 dy/dx = – (2/3)x 1/3 / (2/3)y 1/3 = x 1/3 /y 1/3 = (x/y) 1/3 Hence option (4) is the answerI think your question is (xy—1)/(xy—2)dy/dx=(xy1)/(xy2)(I) Solutionput (xy)=v then differentiate both sides with respect to 'x' we get 1dy/dx=dv/dx




Solution Solve The Differential Equation X Y 1 Dx X 1 Dy 0 If




Misc 7 Show That General Solution Is X Y 1 A 1 X Y 2xy
(x 1) d x d y − y = e 3 x (x 1) 3 Similar Problems from Web Search Find a solution to the following ordinary differential equation \frac{dy}{dx}=e^{x−y}(e^x−e^y)Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Solve (3xy y^2)dx (x^2 xy) dy = 0 , y(1) = 1Substituting y 3 = t so the equation will be 1 3 d t d x ( 2 x 2 − 1) t 3 x ( 1 − x 2) = a x 3 3 x ( 1 − x 2) after this the integrating factor is 1 x 1 − x 2 But I am unable to solve it forward calculus ordinarydifferentialequations Share




Math 432 Hw 2 5 Solutions Pdf Free Download
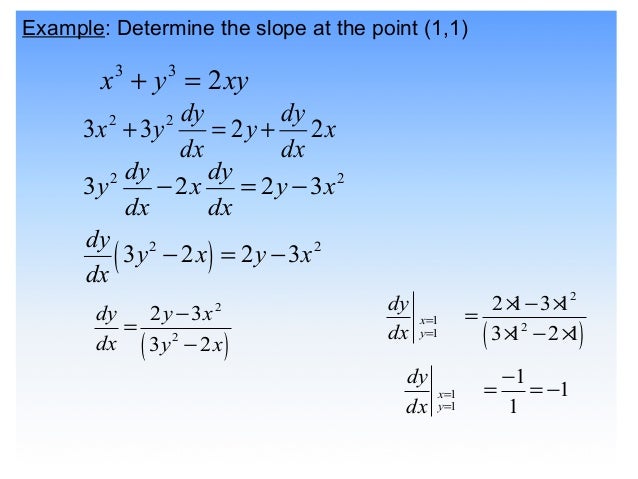



4 1 Implicit Differentiation
If X^2 Xyy^3 = 0, Then, In Terms Of X And Y, Dy/dx = 2x Y/x 3y^2 X 3y^2/2x Y 2x/1 3y^2 2x/x 3y^2 2x Y/x 3y^2 1Verify that x^2 cy^2 = 1 is an implicit solution to \frac {dy} {dx} = \frac {xy} {x^2 1} If you're assuming the solution is defined and differentiable for x=0, then one necessarily has y (0)=0 In this case, one can easily identify two trivial solutions, y=x and y=x If you're assuming the solution is defined andResolver la ecuación diferencial dy/dx= ( (y1) (x2)* (y3))/ ( (x1) (y2)* (x3)) Agrupar los términos de la ecuación diferencial Mover los términos de la variable y al lado izquierdo, y los términos de la variable x del lado derecho de la igualdad




Math 432 Hw 2 5 Solutions Pdf Free Download




Prove That X2 Y2 C X2 Y2 2 Is The General Solution Of The Differential Equation X3 3xy2 Dx Y3 3x2y Dy Where C Is Parameter Mathematics Shaalaa Com
Free Multivariable Calculus calculator calculate multivariable limits, integrals, gradients and much more stepbystepFind dy/dx y= (x^2)/ (3x1) y = x2 3x − 1 y = x 2 3 x 1 Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y) = d dx ( x2 3x−1) d d x ( y) = d d x ( x 2 3 x 1) The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′ y' y ′ Differentiate the right side of the equation Tap for more steps\frac{dy}{dx}=1x^2y^2, Given Here, \frac{dy}{dx} represents the derivative of y with respect to x I will solve for x and y, treating y as a function of x (essentially y=f(x)) \int \frac{dy}{dx}dx=\int 1x^2y^2dx



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Digitalservices Pdf Ap Ap16 Calculus Ab Q4 Pdf




X 2 3y 3 X 2 Y 2 25 0 Novocom Top
862 views around the world You can reuse this answer Creative Commons LicenseSorry, but I didn't had time to type those math\displaystyle \LaTeX/math , so wrote on paper and snapped its picture p > The solution could be very short, butTo ask Unlimited Maths doubts download Doubtnut from https//googl/9WZjCW `(1x^2)dy/dx2xy=(x^22)(x^21)`




Math 432 Hw 2 4 Solutions




If Y 3 U 2 U And U 4x 1 X 2 Find Dy Dx Brainly In
Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, musicThis is the Solution of Question From RD SHARMA book of CLASS 12 CHAPTER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS This Question is also available in R S AGGARWAL book of CLASS Solve the differential equation x(1 – x^2)dy (2x^2y – y – 5x^3)dx = 0 asked in Differential equations by KumariMuskan ( 339k points) differential equations



If Yx Ey X Prove That Dy Dx 1 Log Y 2 Log Y Studyrankersonline




Worked Example Implicit Differentiation Video Khan Academy
To ask Unlimited Maths doubts download Doubtnut from https//googl/9WZjCW Solve `(xy1)dx (2x 2y3)dy=0`Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, musicBernoulli's equation has form, \frac{dy}{dx}p(x)y=q(x)y^n Now, consider this, \frac{dz}{dx}z^2x=z^2z This easily simplifies to, \frac{dz}{dx}z=(1x^2)z^2 where p(x)=1 Bernoulli's equation has form, d x d y p ( x ) y = q ( x ) y n Now, consider this, d x d z z 2 x = z 2 z This easily simplifies to, d x d z − z = ( 1 − x 2 ) z



How To Solve 1 X 3 Dy Dx X 2 Y Quora



Www Ualberta Ca Csproat Homework Math 334 Assignment solutions Assignment 2 solutions Pdf
Ejercicios EDO's de primer orden 3 1 y3 dy = dx x2 Z y−3 dy = Z x−2 dx, 1 −2 y−2 = −x−1 c 1, −1 2y2 −1 x c 1, 1 y2 2 x c, c = −2c 1 Solución implícita 1 y2 2xc x Solución explícita y = ±See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer Previous question Next question Transcribed Image Text from this Question dy/dx = y^2 Sin x^2, y (2) = 1/3 Get more help from Chegg Solve it with our calculus problem solver and calculatorOn dividing the given equation by x^2, it becomes y'' 2(1x)/xy' 2(1x)y/x^2 = x, which is a second order linear differential equation of the form y''f(x)y'g(x)y = r(x), where xf(x) and (x^2)g((x) and r(x) are analytic at x=0, ie x=0
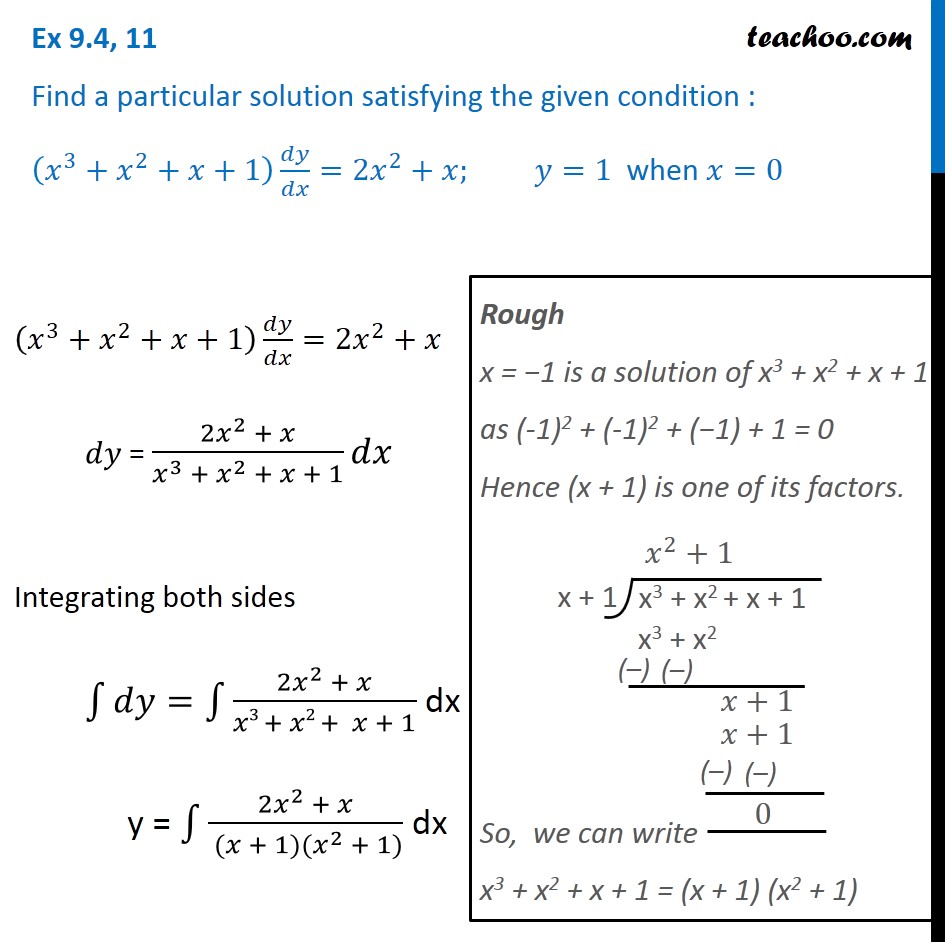



Ex 9 4 11 Find Particular Solution X3 X2 X 1 Dy Dx



Solve 2 Y 3 Xy Dy Dx 0 Given That Y 1 2 Studyrankersonline
Answer to Solve the following equations/IVP 1 (x^3 y)dx xdy = 0, y(1) = 3 2 xy' y = (x y) ln x y/x, y(1) = 2 3 dy/dxWrite the equation as ( (x^2 1 )^3 )dy/dx 4xy( x^2 1)^2 = 1 It can be d/dx( (x^2 1 )(( x^2 1 )^2)y) 2x(( x^2 1)^2)y = 1 Taking (( x^2 1)^2)y=v leads to d/dx(x^2 1)v 2xv = 1 then (x^2 1) dv/dx = 1, separated as dv = dx/(x^2 1 Consider the differential equation dy/dx = x^2(y 1) Find the particular solution to this differential equation with initial condition f(0) = 3 I got y = e^(x^3/3) 2 Calc 2 Find the solution of the differential equation that satisfies the given initial condition dy/dx= x/y, y(0) = −7



Http 1 160 97 198 8080 Xmlui Bitstream Handle 2 2 chapter 1 11 Pdf Sequence 2




How Do You Find Dy Dx For Y 2x Sqrt X 1 Socratic
Calculus Find dy/dx y=1/ (x^2) y = 1 x2 y = 1 x 2 Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y) = d dx ( 1 x2) d d x ( y) = d d x ( 1 x 2) The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′ y' y ′ Differentiate the right side of the equation Tap for more stepsFind dy/dx given x^3 3 x^2 y 2 x y^2 = 12 WolframAlpha Have a question about using WolframAlpha?




Solve 1 X 2 D 2y Dx 2 X Dy Dx Y X 1 X 2 3 2 Mathematics 2 Question Answer Collection



1




Math 432 Hw 2 5 Solutions Pdf Free Download



1



Find The Equation Of A Curve Passing Through Origin And Satisfying The Differential Equation 1 X 2dy Dx 2xy 4x2 Studyrankersonline




Engineering Mathematics Notes




If Y 1 X X 2 2 X 3 3 X N N T H E N Dy Dx




X 2y 3 2xy Dy Dx Novocom Top



Use Fourth Order Runge Kutta Method To Find The Value Of Y At X 1 Given That Dy Dx Y X Y X Such That Y 0 1 Taking H 0 5



Using Euler Rsquo S Method Find An Approximate Value Of Corresponding To 1 Given That Dy Dx X 2 Y And Y 1 When X 0 Use The Step Size H 0 25



1



How To Find Dy Dx Of The Function Y X 1 X 2 X 1 2 Quora



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Digitalservices Pdf Ap Ap16 Calculus Ab Q4 Pdf
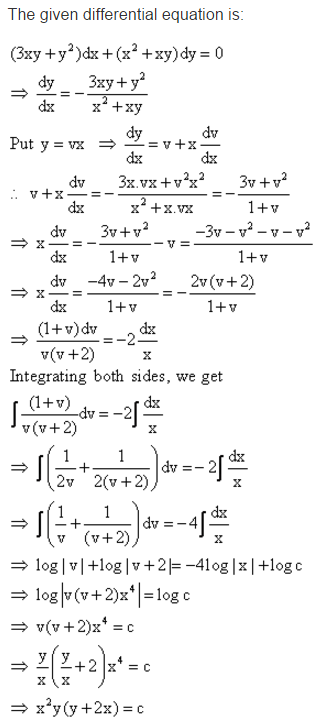



Find The Particular Solution Of Given Differential Equation 3xy Y 2 Dx X 2 Xy Dy 0 At X 1 Y 1 Mathematics Topperlearning Com D1ksg633



What Is The Solution Of This Differential Equation X 1 Dy Dx Y E 3x X 1 2 Quora




Solve The Given Differentia By Separation Of Chegg Com




If 1 X 6 1 2 1 Y 6 1 2 A X 3 Y 3 The Prove That Dy Dx X 2 Y Askiitians



Www Tau Ac Il Levant Ode Solution 6 Pdf




Solve 1 X 2 D 2y Dx 2 X Dy Dx Y X 1 X 2 3 2 Mathematics 2 Question Answer Collection



4 2 Implicit Differentiation




Solve The Initial Value Problem Y X 3 1 Y Chegg Com




Implicit Differentiation



The Differential Equations X 3 X 2 X 1 Dy Dx 2x 2 X Y 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Solucionario Ecuaciones1




Solve X 2 P 3 Y 1 X 2y P 2 Y 3 P 0 Where P Dy Dx Mathematics 2 Question Answer Collection




Misc 14 Find Particular Solution X 1 Dy Dx 2e Y 1



Solve Dy Dx Y 1 X 2 3 2 X 1 X 2 1 2 1 X 2 2 Youtube




Example 9 Find General Solution Of Dy Dx X 1 2 Y Examples




Implicit Differentiation




Answered Sotuions Ii Part A Ane For Which Bartleby



Y 1 Y 2 Y 3 Cheap Online




If Sqrt 1 X 2 Sqrt 1 Y 2 A X Y Show That Dy Dx Sqrt 1 Y 2 1 X 2 Mathematics And Statistics Shaalaa Com




Engineering Mathematics Notes
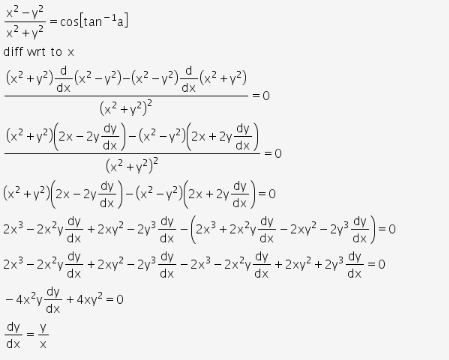



If Cos 1 X2 Y2 X2 Y2 Tan 1 A Prove That Dy Dx Y X Cbse Class 12 Learn Cbse Forum




Solve Y 1 Xy Dx X 1 Xy X 2y 2 Dy 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange




Dy Dx X Y 1 X Y 3 Novocom Top




X 1 X 2 Dy 2x 2y Y Ax 3 Dx 0



Solve The Following Differential Equation 1 1 3 Y X Dy Dx Y 3 X 1 2 Ln X Y X Dx Ln X Dy 3 X 2 Y 2 Y 4sin X Dx 2xy 4y 3cos X Dy 4 Tan X 8sin X Sin Y Dx 8cos X Cos Y Dy 0 5 1 Y 2sin 2x Dx Ycos 2x Dy 0 Wegglab



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Digitalservices Pdf Ap Ap16 Calculus Ab Q4 Pdf
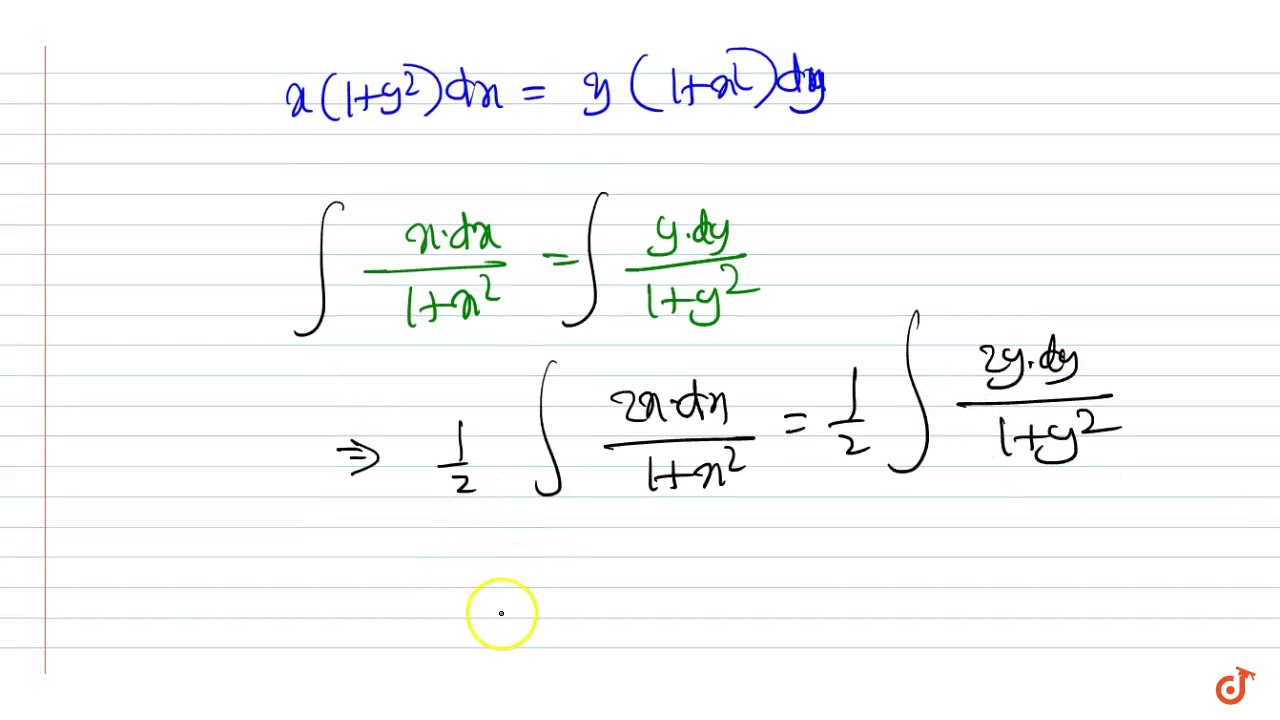



X 1 Y 2 Dx Y 1 X 2 Dy 0 Youtube
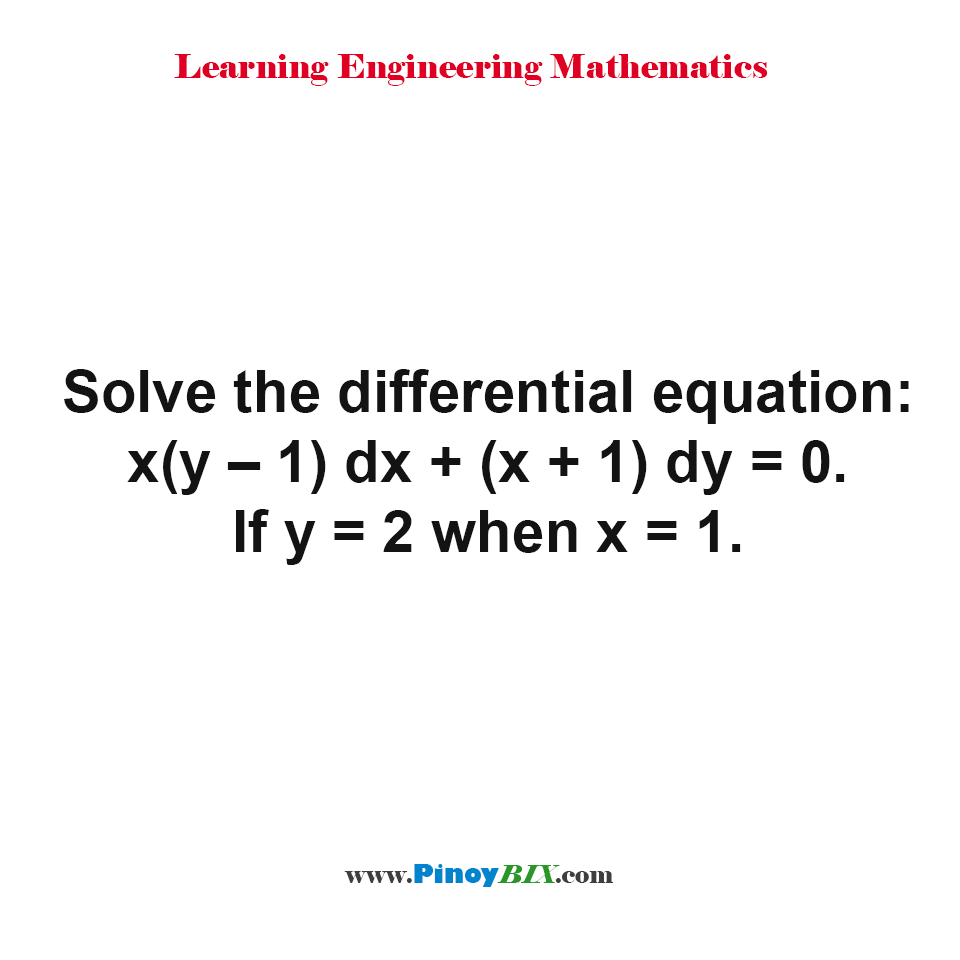



Solution Solve The Differential Equation X Y 1 Dx X 1 Dy 0 If Y 2 When X 1




1 If Y Sqrt X 2 1 Log 1 X Sqrt 1 1 X 2 Find Dy Dx 2 Find The Equation Of Tangent To The Curve Y Sqrt 4x 2 Which




Engineering Mathematics Notes



最新 Xy1 試す




Ex 9 4 16 For Xy Dy Dx X 2 Y 2 Find Solution



Jntua Ac In Gate Online Classes Registration Downloads Material A Pdf




X 1 Y2 Dx Y 1 X2 Dy 0 Brainly In




1 Dy 6x 3 When X 3 And Y 1 Dx D 2 Dy Dx 4x3 3 Gauthmath




Worked Example Identifying Separable Equations Video Khan Academy



4 2 Implicit Differentiation




If Y Root Of 1 X 1 X Then Prove That 1 X 2 Dy Dx Y 0 Brainly In



Find The General Solution Of Differential Equation X 1 Y 2 Dx Y 1 X 2 Dy 0 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Solve The Initial Value Problem Dy Dx Y 1 X 3 Chegg Com




If Y 1 3 X 1 2 X Y 5 1 6 Then Show That Dy Dx Y X Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com



Solved Solve The Following Differential Equations X Y 3 Dx X Y 1 Dy 0 2 X Y 1 Dx 3x 4y 2 Dy C 3 1 Y 2 Xy 2 Dx X 2y Y 2xy Dy Course Hero




Dy Dx X Y 1 X Y 3 Novocom Top




Differential Equations Class 12 Ncert Solutions




Solucionario Ecuaciones1




最新 Xy1 試す




Solve The Initial Value Problems X 2 Dy Dx 4x 2 Chegg Com




Find The Particular Solution Of The Following Differential Equa



Http Www Math Sci Hokudai Ac Jp S Settepanella Teachingfile Calculus Calculus2 Pagine Lineintex Pdf




Solution Of Y Xy 1 Dx X 1 Xy X 2y 2 Dy 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange




The Solution Of The Differential Equation X 3 Dy Dx Y 3 Y 2sqr




Engineering Mathematics Notes
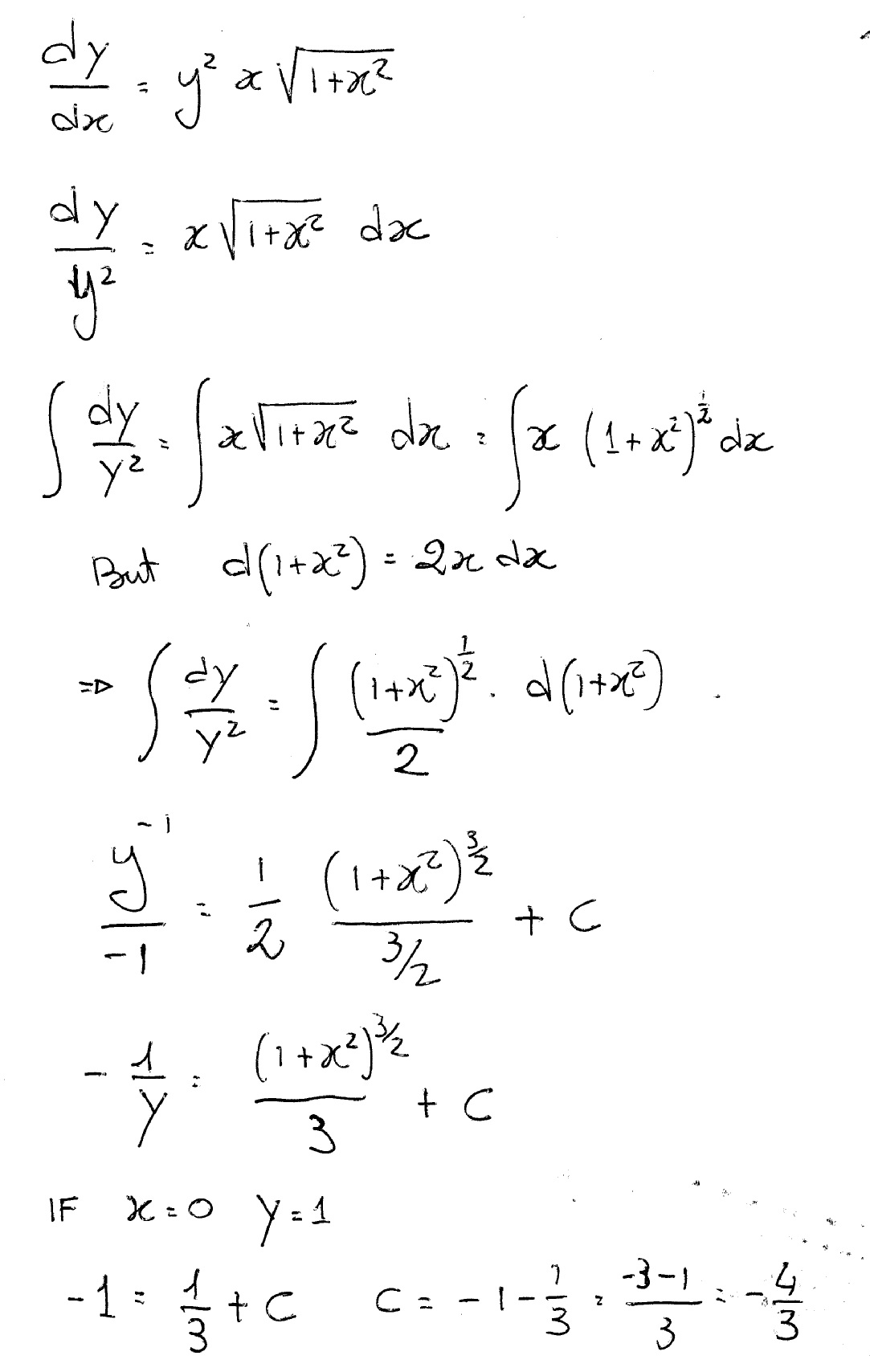



How Do You Solve Dy Dx Y 2xsqrt 1 X 2 Where Y 1 When X 0 Socratic



How To Get The Special Solution Of This Differential Equation Y Xdy Dx 2 1 X 2 Dy Dx Where X 1 Y 1 Quora




Rd Sharma Class 12 Maths Solutions Chapter 11 Differentiation




First Order Differential Equations Chapter 2 Ch2 2 Contents 2 1 Solution Curves Without A Solution 2 1 Solution Curves Without A Solution 2 2 Separable Ppt Download




Differential Equatio Long Answer Questions 7 M R Solye 2x Y 3 Dx 2y X 1 Dy Sol Dy 2x Y 3 Given Equation Is
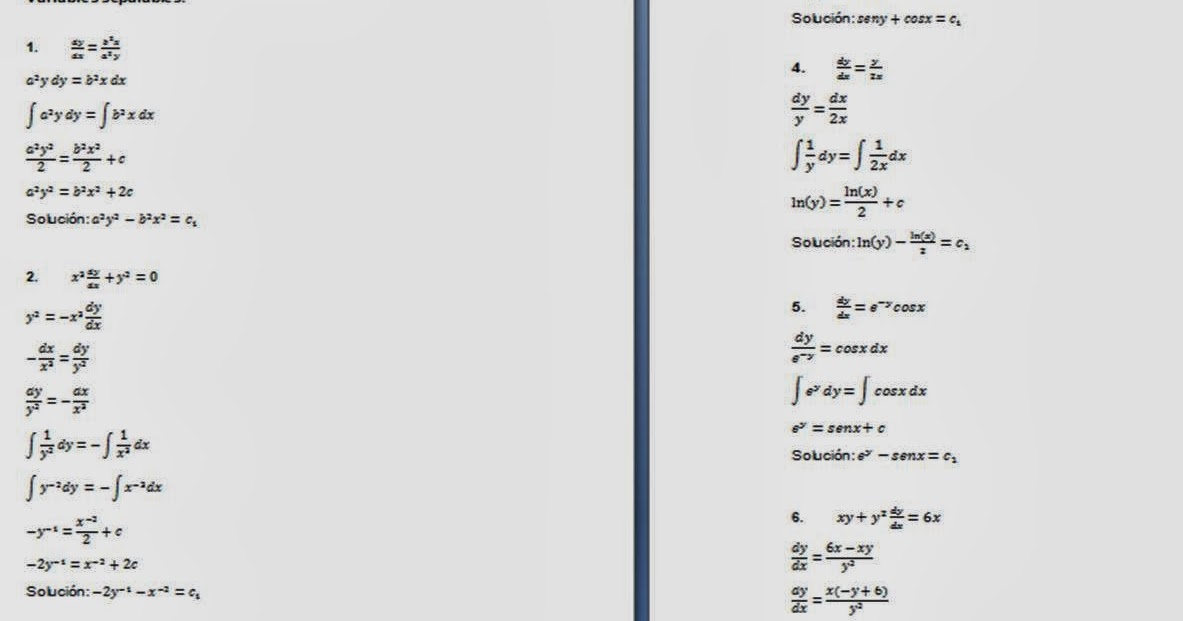



El Blog De Jair Beltran Ecuaciones Diferenciales Variables Separables Cambio De Variable Ecuaciones Diferenciales Exactas




If Y 1 X 1 X 2 2 X 3 3 Then Dy Dx A
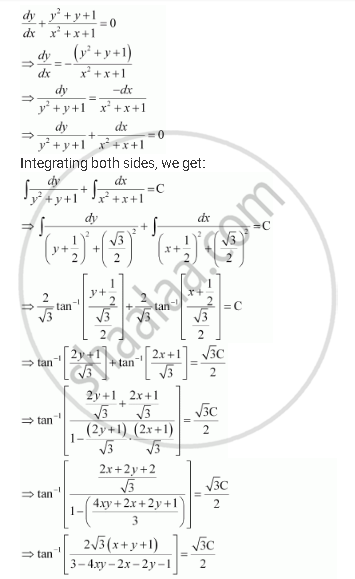



Show That The General Solution Of The Differential Equation Dy Dx Y 2 Y 1 X 2 X 1 0 Is Given By X Y 1 A 1 X Y 2xy Where A Is Parameter Mathematics Shaalaa Com



Www Ualberta Ca Csproat Homework Math 334 Assignment solutions Assignment 1 solutions Pdf




Solve The Differential Equation X 1 Dydx 2x 3y



Answers To The Review Problems For The First Exam 251 05 10 In Spring 06



Solved 3x 8 Y 2 4 Dx 4y X 2 5x 6 Course Hero
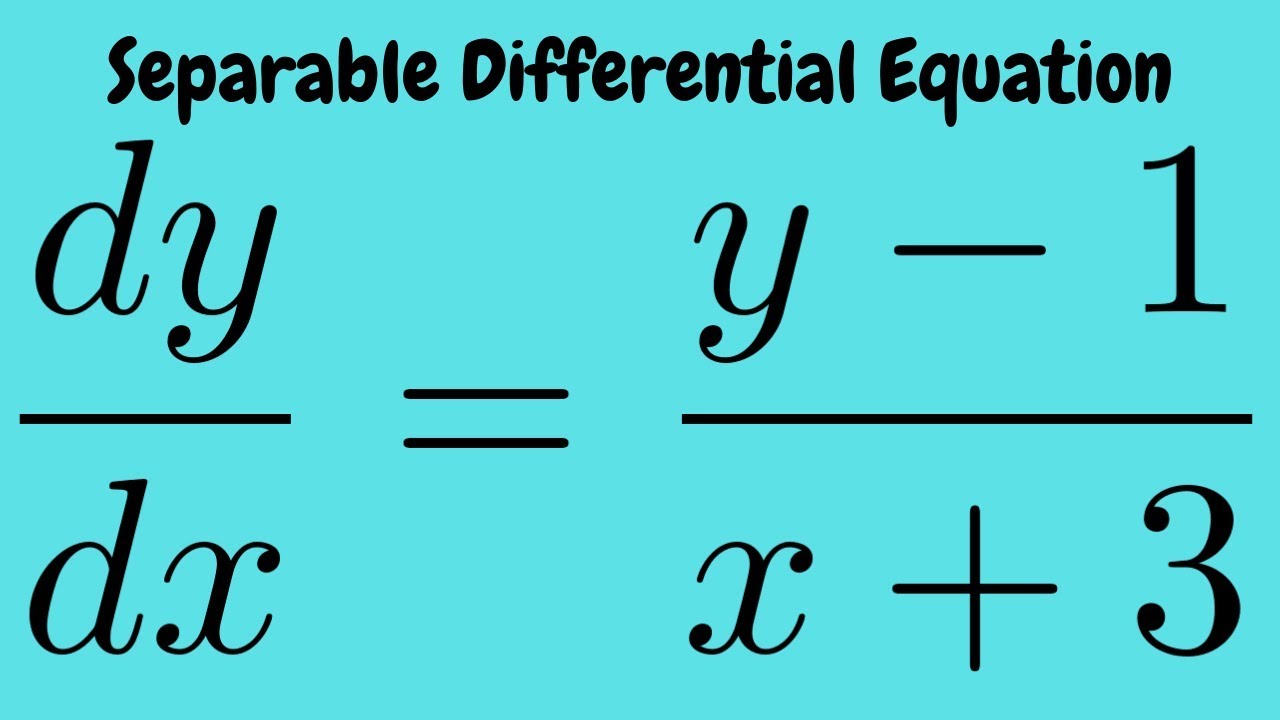



Initial Value Problem Dy Dx Y 1 X 3 With Y 1 0 Separable Differential Equation Youtube




Dy Dx X Y 1 2x 2y 3 Youtube



1



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿